Java String to int conversion can be done using the Integer wrapper class. There are two static methods for this purpose – parseInt() and valueOf().
Table of Contents
Java String to int Conversion Methods
The Integer class provides 5 overloaded methods for the string to int conversion.
- parseInt(String s): parses the string as a signed decimal value. The string should have only decimal digits. The first character can be ASCII minus sign (-) or plus sign (+).
- parseInt(String s, int radix): parses the given string as the signed integer in the radix.
- parseInt(CharSequence s, int beginIndex, int endIndex, int radix): The method is useful in parsing a substring to an integer. If the index values are invalid, IndexOutOfBoundsException is thrown. If the CharSequence is null, NullPointerException is thrown.
- valueOf(String s): This method returns an Integer object. The string is parsed as a signed decimal value. It calls
parseInt(s, 10)internally. - valueOf(String s, int radix): internally calls the parseInt(s, radix) method and returns the Integer object.
Important Points for String to int Parsing
- All the parseInt() and valueOf() methods throw NumberFormatException if the string is not parsable.
- The radix value should be in the supported range i.e. from Character.MIN_RADIX (2) to Character.MAX_RADIX (36), otherwise NumberFormatException is thrown.
- The parseInt() methods return int primitive data type.
- The valueOf() methods return an Integer object.
- The valueOf() methods internally calls parseInt() methods.
- Since Java supports autoboxing, we can use int and Integer in our program interchangeably. So we can use either parseInt() or valueOf() method to convert a string to integer.
- The parseInt() method to parse substring was added to String class in Java 9 release.
- The string should not contain the prefix used to denote an integer in the different radix. For example, “FF” is valid but “0xFF” is not a valid string for the conversion.
- The valueOf() methods are present because it’s present in every wrapper class and String to convert other data types to this object. Recommended Read: Java String valueOf() method.
Java String to integer Examples
Let’s look at some examples for parsing a string to an integer using the parseInt() and valueOf() methods.
1. parseInt(String s)
jshell> Integer.parseInt("123");
$69 ==> 123
jshell> Integer.parseInt("-123");
$70 ==> -123
jshell> Integer.parseInt("+123");
$71 ==> 123
jshell> Integer.parseInt("-0");
$72 ==> 0
jshell> Integer.parseInt("+0");
$73 ==> 0
2. parseInt(String s, int radix)
jshell> Integer.parseInt("FF", 16);
$74 ==> 255
jshell> Integer.parseInt("1111", 2);
$75 ==> 15
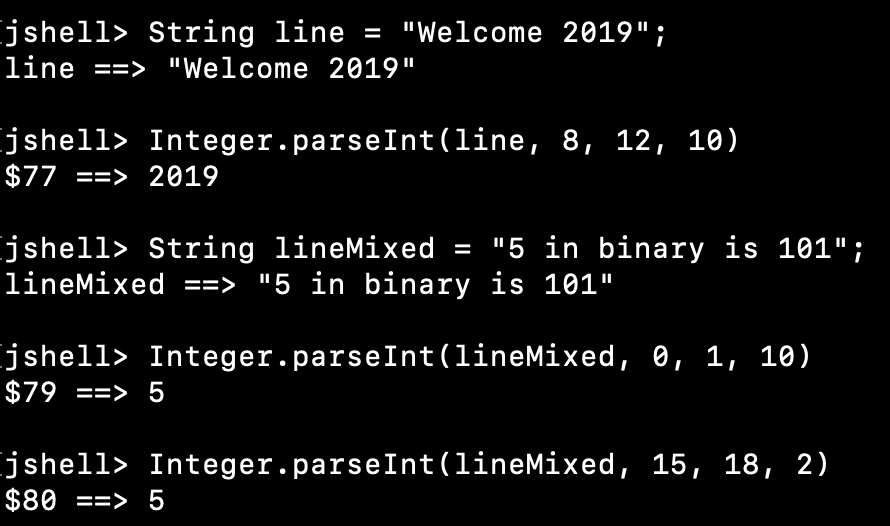
3. parseInt(CharSequence s, int beginIndex, int endIndex, int radix)
jshell> String line = "Welcome 2019";
line ==> "Welcome 2019"
jshell> Integer.parseInt(line, 8, 12, 10)
$77 ==> 2019
jshell> String lineMixed = "5 in binary is 101";
lineMixed ==> "5 in binary is 101"
jshell> Integer.parseInt(lineMixed, 0, 1, 10)
$79 ==> 5
jshell> Integer.parseInt(lineMixed, 15, 18, 2)
$80 ==> 5
4. valueOf(String s)
jshell> Integer io = Integer.valueOf(123);
io ==> 123
jshell> int i = Integer.valueOf(123);
i ==> 123
The valueOf() method returns Integer object. But, we can assign it to int also because Java supports autoboxing.
5. valueOf(String s, int radix)
jshell> Integer.valueOf("F12", 16)
$84 ==> 3858
jshell> int i = Integer.valueOf("F12", 16)
i ==> 3858
jshell> int i = Integer.valueOf("077", 8)
i ==> 63
6. NumberFormatException Example
jshell> Integer.parseInt("abc");
| Exception java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "abc"
| at NumberFormatException.forInputString (NumberFormatException.java:68)
| at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:658)
| at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:776)
| at (#87:1)
jshell> Integer.parseInt("FF", 8);
| Exception java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "FF" under radix 8
| at NumberFormatException.forInputString (NumberFormatException.java:68)
| at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:658)
| at (#88:1)
jshell>
7. NullPointerException when parsing substring
jshell> Integer.parseInt(null, 1, 2, 10);
| Exception java.lang.NullPointerException
| at Objects.requireNonNull (Objects.java:221)
| at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:701)
| at (#89:1)
jshell>
8. IndexOutOfBoundsException when parsing substring
jshell> Integer.parseInt("Hello 2019", 1, 100, 10);
| Exception java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException
| at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:704)
| at (#90:1)
jshell>
9. NumberFormatException when radix is out of range
jshell> Integer.parseInt("FF", 50);
| Exception java.lang.NumberFormatException: radix 50 greater than Character.MAX_RADIX
| at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:629)
| at (#91:1)
jshell>
10. Java String to int Removing Leading Zeroes
If the string is prefixed with zeroes, they are removed when converted to int.
jshell> Integer.parseInt("00077");
$95 ==> 77
jshell> Integer.parseInt("00077", 16);
$96 ==> 119
jshell> Integer.parseInt("00077", 12);
$97 ==> 91
jshell> Integer.parseInt("00077", 8);
$98 ==> 63
Conclusion
Java String to int conversion is very easy. We can use either parseInt() or valueOf() method. Java 9 added another utility method to parse substring to an integer.
